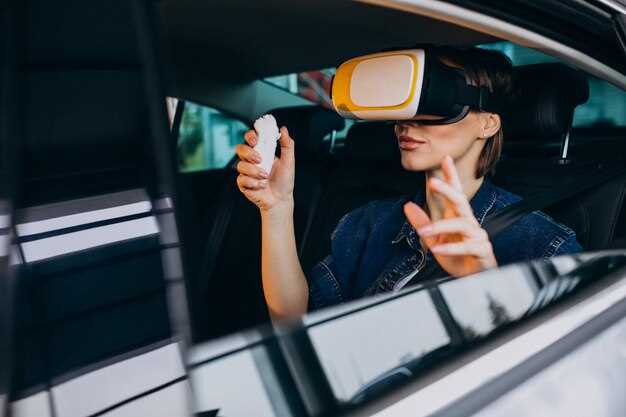

The automotive industry has long been synonymous with innovation, and the integration of virtual reality (VR) into car design is revolutionizing the way manufacturers approach vehicle development. By allowing designers and engineers to immerse themselves in a fully interactive 3D environment, VR technology enhances creativity and streamlines the design process, leading to remarkable advancements in vehicle aesthetics and functionality.
In the context of car design, VR provides an unparalleled platform for visualizing concepts and testing ideas before they become physical prototypes. This capability not only reduces developmental costs and time but also fosters collaboration among stakeholders, enabling real-time feedback and adjustments during the design phase. As a result, the design teams can explore a myriad of possibilities, enhancing the potential for groundbreaking innovations.
The impact of VR on car design extends beyond mere visualization; it reshapes the entire user experience. Designers can simulate driving conditions and user interactions, allowing them to better understand how consumers will engage with the final product. This holistic approach ensures that new vehicles are not only aesthetically pleasing but also functionally superior, aligning with evolving consumer preferences and the demands of modern mobility.
How VR Enhances Collaborative Design Processes in Automotive Development
Virtual reality (VR) has revolutionized the collaborative design processes in automotive development by enabling real-time interaction among designers, engineers, and stakeholders. In traditional workflows, teams often faced challenges in visualizing concepts and communicating ideas effectively. VR eliminates these barriers by creating immersive environments where participants can experience design prototypes as if they were already tangible vehicles.
With VR, teams can collaboratively examine car designs from multiple angles and perspectives. This immersion allows for a deeper understanding of spatial relationships and ergonomics, which are crucial in the automotive industry. Instead of relying on 2D sketches or static models, stakeholders can navigate through a virtual car, simulating the experience of being inside the vehicle. This hands-on experience fosters immediate feedback, facilitating more informed decision-making.
The integration of VR in brainstorming sessions enhances creativity. Participants can sketch ideas in 3D space and manipulate designs instantly, leading to rapid iterations. This collaborative tool breaks down geographical barriers, enabling remote teams to meet in a virtual setting and contribute equally, regardless of their physical location. Such inclusivity promotes diverse input, which is vital for innovative car development.
Moreover, VR allows automakers to conduct virtual reviews with clients and management, showcasing prototypes before physical models are produced. This not only streamlines the approval processes but also minimizes costs associated with physical prototypes. By utilizing VR technology, automotive development teams can efficiently capture and incorporate feedback, ensuring that the final product aligns with market expectations and user needs.
In summary, VR significantly enhances the collaborative design processes in automotive development by promoting immersive visualization, fostering creativity, and facilitating efficient communication. This technology empowers teams to innovate faster and with greater accuracy, ultimately leading to superior car designs that meet the demands of an evolving market.
Utilizing Virtual Reality for Real-Time Prototyping and Testing of Vehicles
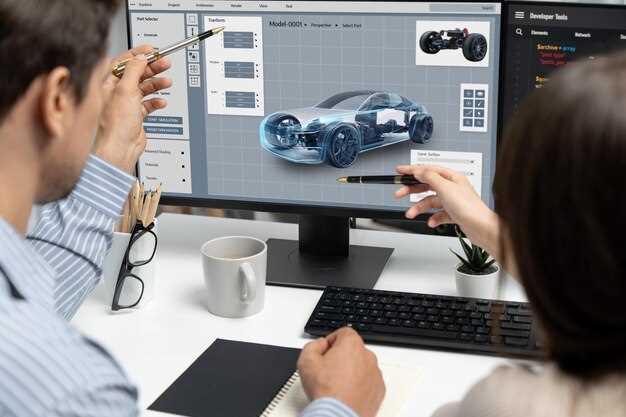
The integration of Virtual Reality (VR) into the car development process has revolutionized the way manufacturers approach prototyping and testing. By creating immersive environments, VR enables designers and engineers to visualize and interact with vehicle models before physical production begins.
One significant advantage of using VR is the ability to perform real-time prototyping. Designers can quickly alter car dimensions, materials, and features in a virtual space, allowing for immediate feedback on design choices. This iterative process significantly reduces the time and costs associated with traditional prototyping methods.
Furthermore, VR allows teams to test different scenarios and conditions without the need for physical vehicles. For instance, engineers can simulate various driving conditions or user interactions to assess performance and safety. This capability enhances the accuracy of evaluations and leads to optimized vehicle designs before they hit the manufacturing stage.
In addition, collaborative features in VR technology enable cross-functional teams to work together regardless of geographical locations. Designers, engineers, and stakeholders can join virtual sessions to explore and discuss car models, ensuring that all perspectives are considered in the development process.
Overall, the utilization of Virtual Reality for real-time prototyping and testing not only accelerates the development timeline but also enhances the quality and innovation of car designs, paving the way for future advancements in the automotive industry.
The Role of Immersive Technologies in User-Centric Car Design
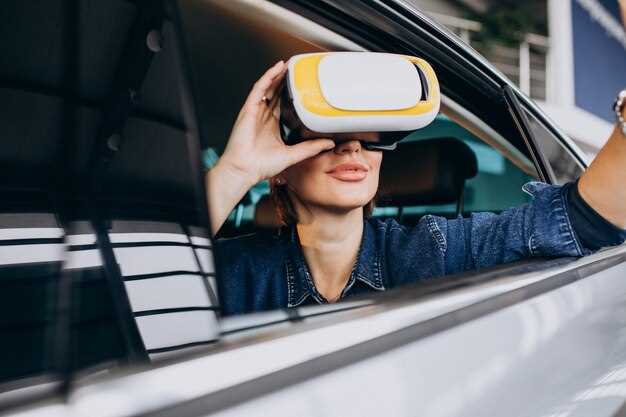

Immersive technologies, particularly virtual reality (VR), have revolutionized the approach to car design by placing user experience at the forefront of the development process. This shift towards user-centric design prioritizes the needs and preferences of drivers and passengers, allowing for a more intuitive and satisfying interaction with vehicles.
In traditional design paradigms, user feedback was often gathered post-design, leading to expensive revisions and modifications. However, with the integration of VR, designers can create immersive environments where stakeholders experience the vehicle before its physical prototype is built. This early testing facilitates immediate feedback, allowing designers to make informed adjustments that align with user expectations.
Moreover, VR enables car designers to explore various design options in real-time, iterating on features such as dashboard layouts, seating arrangements, and infotainment systems. Through immersive simulations, users can interact with car features and assess usability, aesthetics, and comfort, thus ensuring that the final product resonates with the target audience.
The implementation of immersive technologies also extends to accessibility considerations, as designers can simulate different demographics and physical requirements. By understanding how various users will navigate the car space, design teams can create more inclusive and ergonomic solutions.
Additionally, incorporating VR in the brainstorming phase enhances collaboration among designers, engineers, and marketing teams. By visualizing designs in a shared Virtual space, teams can converge ideas, identify potential challenges, and develop a unified vision more effectively.
In conclusion, the application of immersive technologies like VR in user-centric car design fosters innovation, accelerates the design process, and emphasizes user feedback, ultimately leading to more personalized and functional vehicles. This paradigm shift not only enhances customer satisfaction but also positions brands as leaders in a competitive automotive landscape.



